|
Water Power Plants and Water Turbines
MEASUREMENT OF VIBRATION AND TECHNICAL CONDITION ASSESSMENT OF WATER POWER PLANTS:
FRANCIS, KAPLAN AND DERIAZ TURBINES .
Vibration Condition of Water Power Plants
The measurement is limited to that of physical quantity sets which can be used to define and evaluate unambiguously vibration condition of the water power plants.
 |
 |
| Kaplan turbine |
Deriaz turbine |
Such measure is conducted in order to:
- Assess the vibration degree: current condition compared to the history of the water power plants,,
- Collect data to make a complete analysis of the vibration state: current condition compared to the history of the water power plants,
- Interpret the vibration state observed: current condition compared to the history of the water power plants,
- Make a diagnosis regarding the technical state of the turbo set: current condition compared to the history of the water power plants,
- Make a forecast about the future technical state: current condition compared to the history of the water power plants,
- The measurement of the vibration time and the scope of repair serve as a basis for determining the turbine’s state.
Thus, the repair procedure can be planned according to the actual technical condition of the water power plant. Additional advantage of this approach is that it is possible to obtain proper spare parts beforehand. As a result, the time and the scope of the repair can be reduced to a minimum.
Type and Scope of Measurement
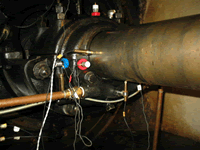 |
| Measurement of vibration of two-rotor Francis water power plant’s guide bearing |
Measurement of an operating turbine set’s vibrations is conducted with:
- a monitoring unit mounted permanently: the so-called turbine set monitoring system,
- sensors of a stationary monitoring system mounted on the turbine set,
- a measuring system installed by us for a longer period of time,
- a measuring system installed by us for a period during which the measurement is carried out,
- a portable measuring apparatus,
In each of the above cases, if necessary, the measuring system can be supplemented with sensors essential for obtaining the best description of the turbine set’s technical condition.
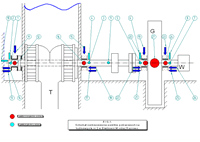 |
| Diagram of the arrangement of sensors on a horizontal water power plant. |
The scope of the measurement we conduct depends on requirements, objectives and technical problems discovered during the operation of the device inspected.
According as the scope of the measurement, we are able to indicate and inspect the following basic faults of a water power plant :
- Flaws of the rotating system balance,
- Flaws of alignment,
- Seizures in seals,
- Looseness in w bearing supports,
- Flaws of the arrangement of bearing supports,
- Misalignment of the rotor in the generator stator,
- Axial displacement of the rotor in relation to the generator’s stator,
- Misalignment of the turbine’s rotor in the chamber,
- Displacement of the rotor along the axis in relation to AK,
- Wrong settings of combinatorial interdependencies,
- Vortex in the chamber of turbine’s rotor,
- And approximately 200 other possible faults of the water power plant.
 |
| Vortex underneath the rotor of the Francis turbine |
We also carry out measurements geared to wards:
We indicate loosenings or any possibility of looseness in the clutch plate mounting on the shaft of the rotor. Measurement is carried out when the rotor is disabled, for example, during a repair of the unit. For this purpose, we use a method developed by the VIBROPOMIAR Company on the basis of modal analysis.
- Locating sources of vibrations and searching for their causes,
- Preparing the scope of repair work: selection of elements which must be inspected in the course of a repair,
- Assessing the vibration condition after the completion of the repair,
- Determining the frequency and the form of free vibration of water power plant’s elements (eg. blade, shaft bossing, turbine’s cover, elements of bearings and their supports etc.) and machines’ units (e.g. pipelines, gates, support system, etc.)
- Measuring and assessing the influence of the flowing water on the vibration condition of water power plants (influence of the hydraulic input),
- Assessing the influence of electromagnetic inputs of the generator on the dynamic state of the water power plant,
- Detecting any possible looseness of the sheet packs of the generator’s rotor while it is spinning,
- Searching for causes of instability of the rotating system’s motion,
- Setting optimal combinatorial interdependencies,
- Eliminating all unfavourable and untypical phenomena occurring during the operation of water power plants.
Moreover, we determine the ranges of actual critical velocities of water power plants’ rotors.
We also establish the frequencies of free vibrations of the water power plant’s main elements. Elements whose free vibration should be measured include: (Link to the article) :
- Load-bearing truss of the generator or the engine,
- Body of the stator of the generator or the engine,
- Cover of the turbine’s rotor chamber,
- Blades of the managing apparatus,
- Blades of Francis turbine’s rotor,
- Blades of Kaplan turbine’s rotor,
- Torsional vibration of the lower hoop of the Francis turbine’s rotor,
- Vibration of the unit’s shaft – transverse, torsional and oscillatory vibrations,
- Shaft bossing of the turbine’s rotor,
- Inlet pipeline,
- Oil pipeline and other construction joints.
In this way we provide a team operating the water power plants with the knowledge of what ranges of inducement frequencies are dangerous for a given construction joint. Such measurement is aimed at improving the safety of operation.
The VIBROPOMIAR Company also maintains a measuring team which responds to emergencies. It conducts limited measurement consisting of the evaluation of the rotating system’s vibration condition. This measurement serves the purpose of assessing fitness of a rotating system for further operation, making it possible to evaluate its technical condition .
New products

|







